Why is photosynthesis required?
Definition:
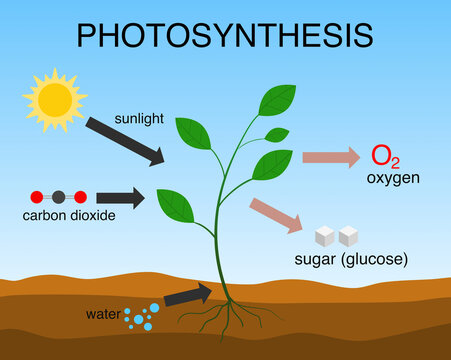
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in the form of glucose (sugar) and other organic compounds. This process is fundamental to life on Earth as it provides the energy and organic molecules necessary for the growth and survival of plants and many other organisms in the food chain.The basic equation for photosynthesis is:
6 CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6 H2O (water) + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 (oxygen)
Photosynthesis occurs primarily in the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically within the thylakoid membranes. The process can be divided into two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle).
1) Light-Dependent Reactions:
In the thylakoid membranes, chlorophyll and other pigments capture light energy from the sun. This energy is used to split water molecules into oxygen and protons (H+), releasing oxygen as a byproduct. The energy is also used to create energy-rich molecules, such as ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are crucial for the next stage.
2) Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reactions):
In the stroma of the chloroplasts, the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose through a series of chemical reactions. This process is called the Calvin cycle. The cycle involves a sequence of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that ultimately build glucose and other organic compounds using the captured carbon dioxide.
Photosynthesis not only produces glucose, which serves as a source of energy for plants and other organisms, but it also releases oxygen into the atmosphere, contributing to the oxygen-rich environment that supports aerobic respiration in animals and other organisms.
In summary, photosynthesis is a vital biological process that plays a central role in the Earth's ecosystem by converting solar energy into chemical energy and providing the foundation for the food chain and the oxygen we breathe.
Very helpful
ReplyDelete